Cultivation procedure
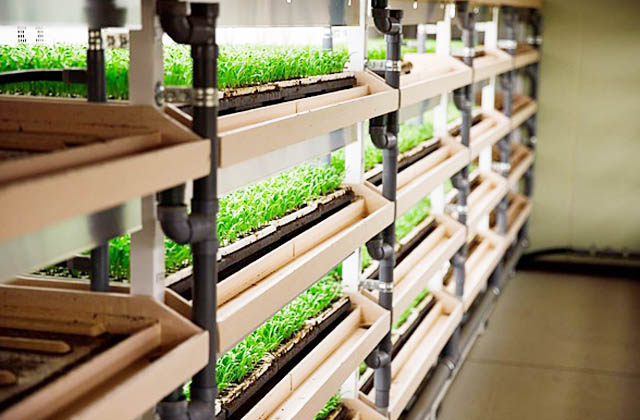
raising of seedling
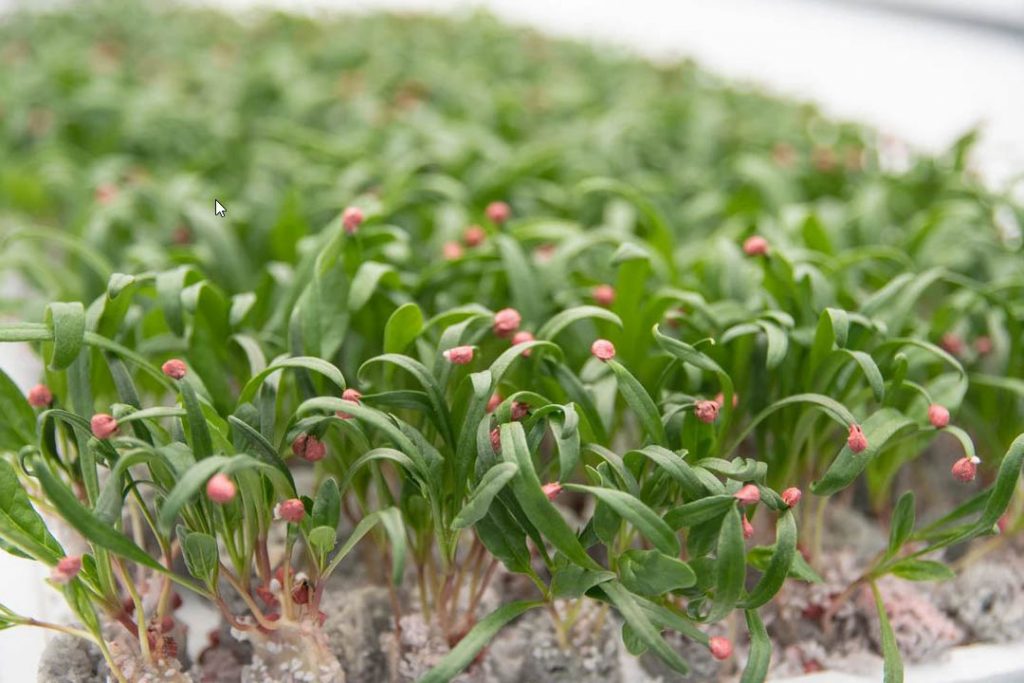

(1) Sowing and pre-germination management
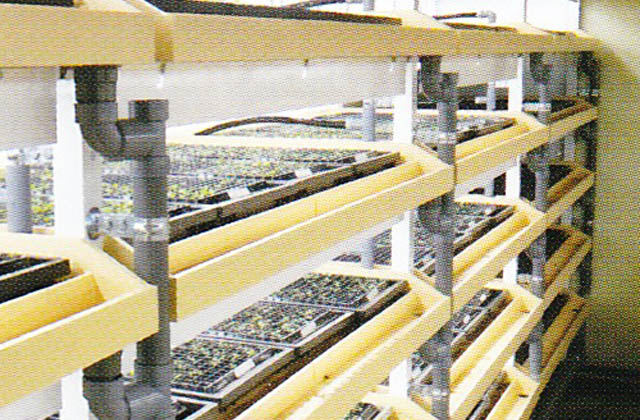
Fill seedling trays (144 holes) with a special medium consisting mainly of rockwool granulated cotton and make sowing holes with a press board. Sow 4 to 5 seeds per cell using a sowing board. After covering with soil medium, apply 300ml to 400ml of water per tray, and seeds are germinated in a germination chamber (set at 20°C) for 3 to 4 days.
(2) Seedling management
After germination, take out the trays and place them on the racks of NAE TERRACE. Automatically apply 300 to 400 ml of nutrient solution per tray twice a day during the high temperature season and once a day during the medium to low temperature season. The concentration of nutrient solution should be electrical conductivity (EC) of 1.3 dS/m in the high temperature season and EC of 1.5 dS/m in the low to mid temperature season.
transplanting
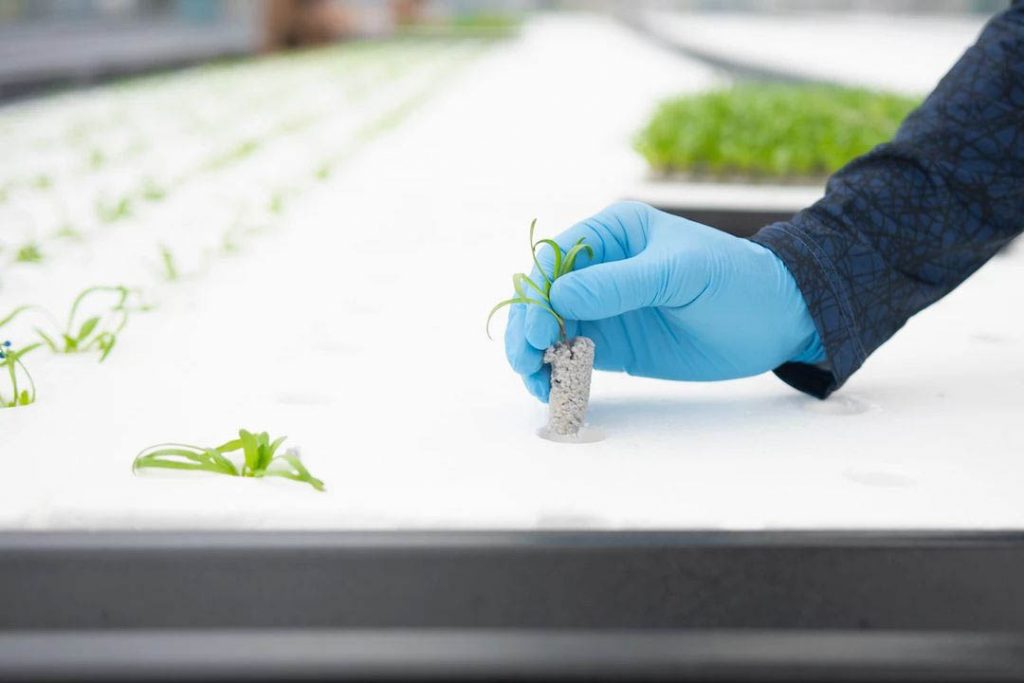

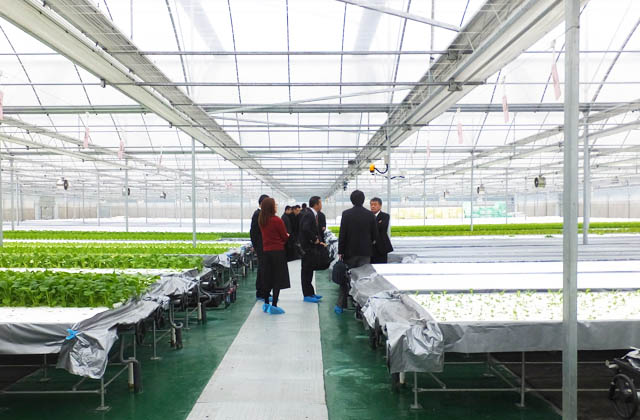
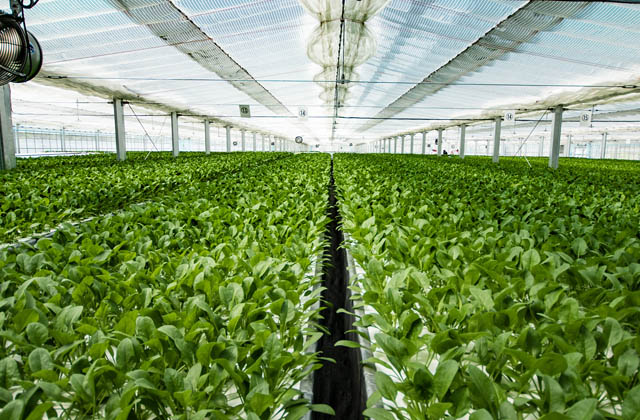
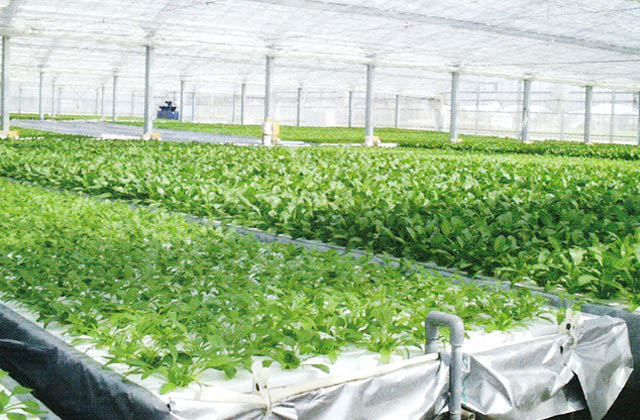
Set up a new nutrient solution to be grown in the growing block (4 to 6 growing beds with 500 l culture tanks, water supply and drainage system; divide the beds into 10 to 16 blocks per 16 a.). The best time to plant is when the first two leaves have grown to about 3 cm in length. Prior to planting, the seedlings are pushed up using a seedling puller. To plant, simply pick up the seedlings and drop them into the planting holes on the planting panel. The seedlings are supported by the bottom of the bed and stand on their own. The number of planting holes is 45 per panel (1 x 0.6 m). The seedling rootpots are placed in a humid space and begin rooting immediately.
cultivation management
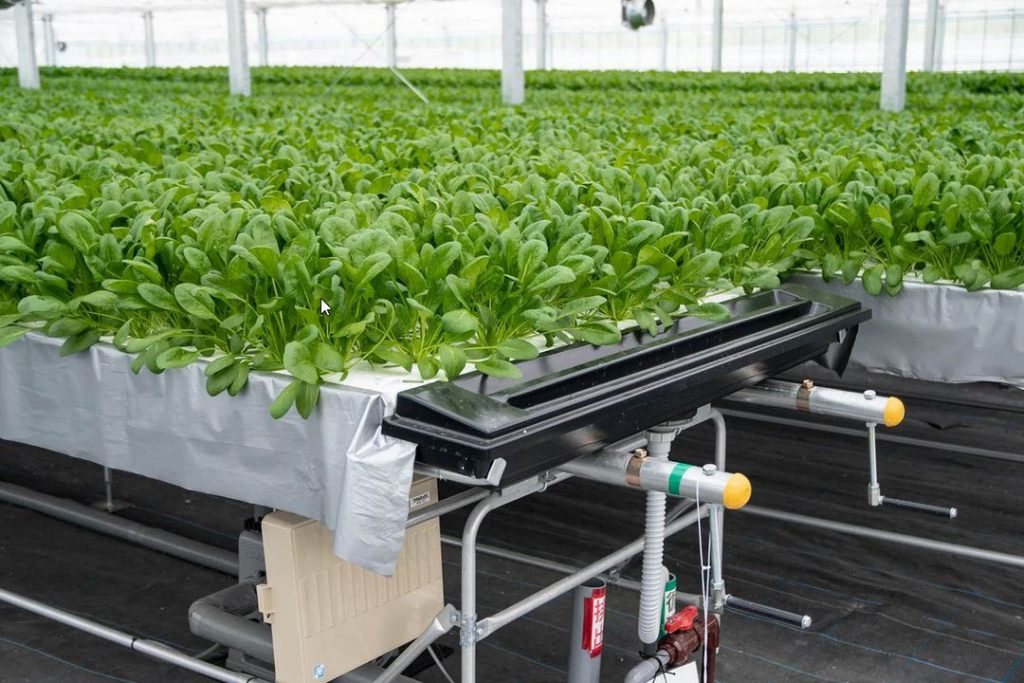

(1) Composition of the nutrient solution
Spinach plants absorb a large amount of NO₃-N and K and a small amount of Ca . The apparent absorption concentrations are approximately NO₃-N: 16me, P: 4me, K: 12me, Ca: 4me, and Mg: 4me/l. Supplied solution should be adjusted with liquid fertilizer using these figures as targets (taking components of raw water into account).
( 2 ) Concentration of the nutrient solution
The EC of the starting and supplemental nutrient solution should be 3 dS/m. As the plants grow, the EC decreases, reaching around 1.2 dS/m 2 to 3 days before harvest. At this time, if the culture solution supply is stopped and only water is supplied, the fertilizer component will be almost completely absorbed by spinach plants by the time of harvest. There is no waste of fertilizer, and the residual solution can be disposed of without polluting the environment.
(3) pH of the nutrient solution
The ideal pH of the nutrient solution is 6 to 6.5. The pH increases slowly during cultivation and does not need to be adjusted if it is in the range of 5.5 to 7.3.
(4) Temperature of nutrient solution
The temperature of the nutrient solution should be kept below 23°C in spring and summer. To cool the nutrient solution, well water or chiller cooled water should be flowed into the heat exchanger inside the tank. (Keep the temperature above 10°C in winter.)
(5) Water supply
The amount of liquid supplied per bed is 9 liters/minute and is continuous. The nutrient solution tanks of each block are automatically supplied from the main tank with the standard nutrient solution.
(6) Oxygen supply
Since the structure is designed to allow the roots to use the aerial oxygen in the bed, there is no need to take this into consideration.
(7) Environmental management of aerial part
Spring and summer seasons should be actively ventilated (an extremely important task). Ventilate during the night as well. Shade nets (20-30% shading) should be spread on sunny days from May to October, and should be fixed in July and August, but opened in case of continuous cloudy and rainy weather.
(8) Crop management
There is no particular harvest.
| Underground part | EC target | 3.0 at transplanting → 1.2 for 2 days before harvest → 0.8 at harvest |
| pH target | 5.5 to 6.5 is ideal | |
| Temperature of growing solution | Cooled with well water or chiller cold water, kept below 23°C | |
| Other controls | Nutrient solution supply is continuous |
| Aerial part | Temperature in the greenhouse | Keep ventilation during the day and night |
| Carbon dioxide concentration | natural | |
| Light environment | 20-30% shading netting is used, fixed in July and August. |
| Chemicals for disease and pest control | The cultivation will be completely pesticide-free. The cultivation equipment and materials are heat sterilized. |
disease and pest control
Take care of damping-off caused by Pythium and wilt caused by Fusarium. After cultivation, sterilize the beds. Place a new nutrient solution after cleaning the beds and cover the beds with a film. Heat the nutrient solution to 60°C using a boiler and circulate it in the beds for one hour. This sterilizes the bed, tank, and pipes. This method is simple and effective. Aphids and armyworm sometimes occur, but they do not cause serious damage. No pesticides are used.
harvesting
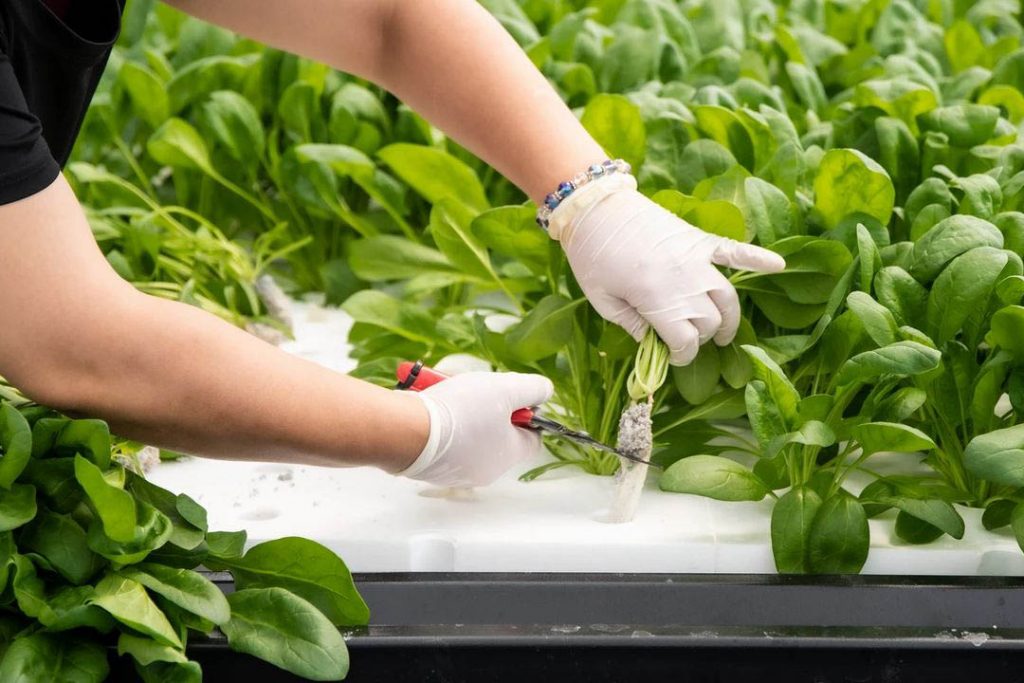

When the leaves reach 25 to 30 cm in length, harvest the plants with the medium attached. Harvesting early in the morning is preferable. The packing method should be decided after discussing with the customer. Since there are no dead leaves, it is enough to remove only the cotyledons when removing the lower leaves. Store in a pre-cooler except when preparing for removing procedure.
Business Management
Around 15 cultivations per year, yielding about 30 tons per 1818 m2 (550 tsubo), with a total work time of about 7,000 hours. If the unit price of spinach per kilogram is 700 yen, sales are estimated to be around 21 million yen, and after deducting management costs (including depreciation, wages, and interest), gross income per 1.5 core workers is expected to be 20 to 25% of sales. Fertilizer costs are expected to be around 1,500 yen/3.3m2(1 tsubo) at around 3 tons per 10a, since fertilizer costs can be saved in the remaining fertilizer treatment process.